Blog
CNC Machines: Everything You Need To Know
The role of CNC machines in industrial and manufacturing segments is considerable. They are computer-controlled and offer a level of reliability, consistency, accuracy, and efficiency that would not be achievable through manual processes.
It is estimated that by 2025, the CNC machinery market will reach over 100.9 billion worldwide. Nowadays, CNC machining is a typical part of many industrial manufacturing processes due to its significant role in increasing production.
It also provides a greater range of applications than manually operated machinery.
This article will explain everything you need to know, from details to the function of these machines.
What exactly is the meaning of CNC machines?
The term “Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines” refers to a computerized manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software and codes control the movement of production equipment and tell the machine how to move factory tools and machinery. These devices represent a manufacturing procedure that is used to manage numerous intricate tasks.
We use CNC machining in many different industries; however, it is most prevalent in metal and plastic production. It can complete three-dimensional cutting tasks with a single set of prompts and, consequently, minimal assistance from human operators.
These machines work like robots; once you put programming into the machine, it will operate automatically, and the software will control its speed, machinery, and involved tools.

NCM machines vs. CNC machines
Here is the focal question: what is the difference between CNC and NCM machines?
NCM stands for “Numerical Control Machine,” referring to the particular types of programming in which programs are input through the computer punch cards. To enter codes into CNC machining, we use small keyboards.
An NCM machine can only execute the current task through punch cards. While a CNC machine stores the program on the computer and then completes its task automatically (rather than manually entering a card).
Thanks to human programmers and retained computers, the computational capacity of these machines is extendable.
Keep in mind that CNC programming is expensive. By revising the code, you can add new programs to pre-existing programs.
CNC machine programming
As mentioned before, the function of these machines highly depends on programming, and a human programmer should input the proper code to ensure it works properly.
The language behind CNC machining is the complex programming language known as G-Code, which controls many varying behaviors, including speed, coordination, feed rate, etc. Once you put G-Code in the machine, there is no need for a human operator because the code does most of the work.
Most manufacturers producing these parts have code to put into the machine for one or two functions.
Programming CNC Machines: Steps
The language behind CNC machining is the complex programming language known as G-Code, which controls many varying behaviors, including speed, coordination, feed rate, etc. Once you put G-Code in the machine, there is no need for a human operator because the code does most of the work.
Most manufacturers producing these parts have code to put into the machine for one or two functions.
The basic process of CNC programming is simple. The most challenging part is learning, understanding, and developing it.
Here is a brief explanation of the programming:
- Step 1. A two- or three-dimensional computer-aided drawing is convincing. This drawing will be of the desired final product.
- Step 2. The computer-aided drawing is translated into computer code to enable the CNC machine to read and execute the desired functions.
- Step 3. The machine operator will give the new code a trial run to ensure it runs smoothly without errors or mistakes.
- Step 4. The process will be complete if the machine programming works without error. If there is any mistake in the G-Code, the operator should fix it. After rectifying the error, the operator will retest the machine.
After activating the system, the desired cuts will be programmed into the software to tell the corresponding tools and machinery what to do.
Error in a CNC machine
CNC machining, despite all its benefits, is not perfect. The assumption of perfection is their biggest drawback. The code generator inside the system often gives us the false perception that the system works flawlessly. Although the possibility of errors is common, certain situations increase the risk of them; for example, when you give the machine a code to cut in more than one direction at the same time.
Application of CNC Machines
You may wonder if you know the earliest use of numerical control technology dates back to the 1940s when we began using motors to control the tools’ movement, giving birth to a mechanism that can be controlled by a computer.
In the modern age, we see the birth of digital computer technology to create CNC machining by applying the technology to pre-existing NCM technologies.
The work of many industries has become easier with the increasing capabilities of CNC machines. These machines have been designed to work with various materials like metal, plastic, glass, wood, composite, and foam.

Different types of CNC machines
CNS Mills runs using programming, and it can use both numbers and letters.
The programming guides the various machine elements along different distances. The basic models work on a three-axis system; however, the newest models are more complicated and can operate up to a six-axis system.
lathes
With the help of indexed tools, a lathe CNC machine can cut pieces in a circular direction with velocity and precision.
We use lathe machines to produce a complex design for manually operated machinery. Despite its complicated design, the lathe is a relatively simple machine. A two-axis system is the most common lathe machine.
Plasma Cutters
When you work with metal materials, plasma cutters are the best. To make a precision cut in metal, you need lots of speed and heat. We need a combination of compressed air gas and electrical arches to achieve this level of heat and speed.
Wire Electric Discharge Machine (EDM)
These machines use electrical sparks to shape a model. To remove portions of naturally electronically conductive materials, use spark erosion.
Sinker EDM (Electric Discharge Machines)
The operation of sinker EDMs is similar to that of EDMs, but sinker EDMs use electricity to remove pieces. Sinker EDM has molded materials into specific shapes by soaking them in a dielectric fluid to conduct electricity.
Water jet cutters
We use this machine to cut hard materials (often metal and granite) with high-pressure water. Sometimes, for more cutting and shaping power (without adding heat), we use a mixture of sand or other abrasive materials in the water.
CNC Drilling Machines
These machines use multiple-point drills to create circular holes in the workpiece. To create vertical holes, use drill bits perpendicular to the workpiece’s surface. We can also program the process to make angular holes.
CNC machine wood
When it comes to woodworking, this machine offers the best precision and speed.
Wood Computer numerical control (CNC) machines are electro-mechanical devices that allow you to control machine shop instruments like drills and lathes via programming inputs.
The tool will position above the work surface and move along the X, Y, and Z axes to carve the wood into the desired shape.
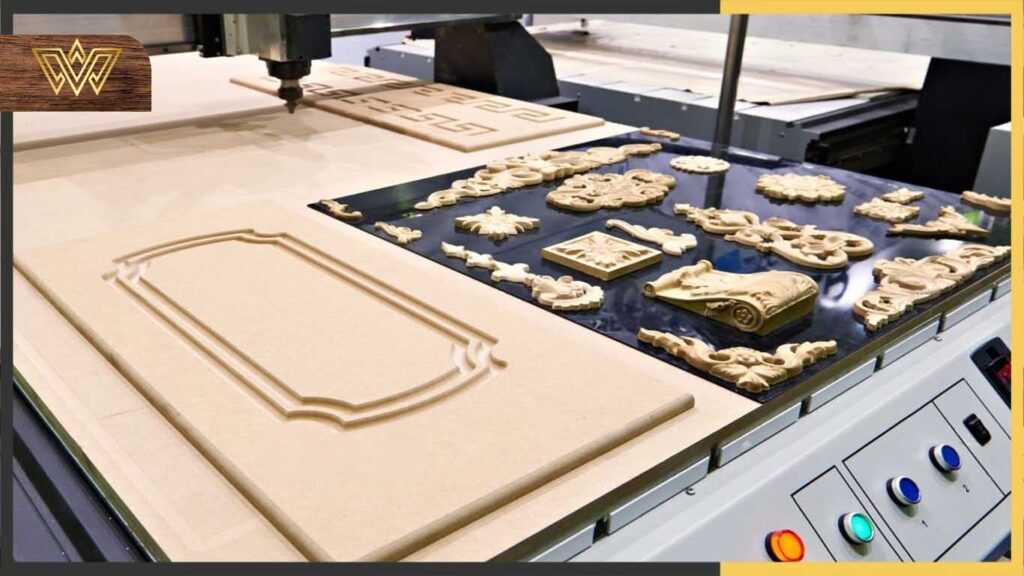

The advantages and disadvantages of wood CNC Cutting Machine
Advantages:
- CNC machine wood cutting offers rapid prototyping, reduces production time and errors, and creates nearly identical products every time.
- Enhances the versatility of your portfolio by engraving and carving various materials such as plastics, metals, stones, and acrylics.
- You will not need many people to operate the machine, meaning you will need to hire a few employees if you are a business owner.
- It is ideal for all individuals at any skill level.
- Save money and time.
Disadvantages
- If you do not maintain it properly, you will incur considerable upfront costs and potentially costly repairs.
- Leftover dust can harm the machine if it is not well-shielded.
Some of the best home CNC machines
Carbide3D Nomad 3
It is the perfect router for both consumers and prosumers, ensuring noise and dust stay inside the enclosure. It has a completely aluminum frame and a sturdy rigid base that reduces unwanted vibration.
The Nomad3 suits those who do not need a massive build volume and want a desktop CNC router that produces top-notch outcomes.
Benefits:
- Enclosed work area
- Rigid frame
- Desktop size
- No assembly is needed.
Drawbacks:
- There is no dust collection system.
- Limited upgradability
SainSmart Genmitsu 3018-PROVer
It has an aluminum body that gives the machine a professional look and ensures structural rigidity. We bravely announce that there is no home CNC with that capability at this price in the current market.
Engineers, woodworkers, and other professionals find it perfect because of its sturdy construction, high-quality accessories, and sizable working surface.
Benefits:
- Low-cost
- Lots of compatible accessories
- Easy for beginners
Drawbacks:
- Quality control problems
- Small working area
Lastly
One of the best and most well-equipped workshops in the GTA is Woodyart Workshop. In our workshop, we have several CNC cutting machines that are all equipped with Biesse CNC cutting systems.
High-performance, adaptable CNC woodworking equipment for large-scale industrial applications and carpentry are the distinctive features of our machines.
Contact us if you need more information and guidelines.

FAQ
CNC manufacturing uses computer programs to control machine tools that produce high-quality, precise, and close-tolerance parts. The manufacturing process enables predictable, accurate outputs while freeing up labor for other duties.
In the CNC process, computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software are written in proprietary languages named G-Code and M-Code. These programs regulate features such as cutting speed, piece placement, and raw material feed rate.
The term "hobby CNC router" refers to a particular type of small CNC machine for hobbyists with a mini-table size that is controlled by a computer or DSP. It is also known as a mini CNC router, desktop router, entry-level router, mini router, portable router, tabletop router, etc.
CNC Machine Metal uses a computer numerical control (CNC) system to shape it, like bending, turning, grinding, extruding, milling, etc.












